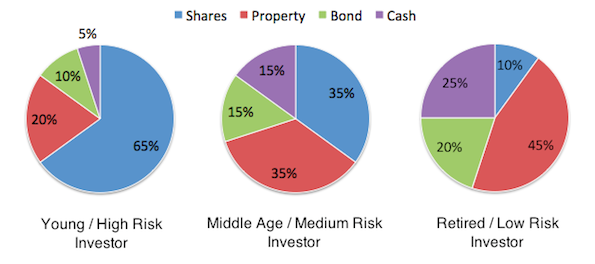
Investing wisely is key to achieving financial freedom, but determining how to allocate your assets among stocks, bonds, and cash can be challenging without a clear plan. Your age, risk tolerance, and financial goals are crucial in shaping your ideal portfolio. Younger investors can take more risks with higher stock exposure, while older investors should focus on stability through bonds and cash. Understanding the right asset allocation by age helps balance growth and security, ensuring long-term success and steady returns throughout different life stages.
Key Factors That Influence Asset Allocation


1. Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance refers to how much financial uncertainty or loss you can handle when investing. It depends on your personality, income stability, and financial responsibilities. Understanding your comfort level with market ups and downs helps you choose the right investments that match your peace of mind and long-term goals.
2. Time Horizon
Your time horizon is the period you plan to keep your money invested before you need it. A longer time horizon allows you to take more risks for higher potential returns. If your goal is short-term, you should focus on safer investments to protect your money.
3. Age
You must understand asset allocation by age. If you are a young investor, you can afford to take on more risk with a higher stock allocation, as you have enough time to recover from downturns. However, older investors have different financial goals. They try to reduce their risk by shifting to lower-risk assets, such as bonds and cash.
For more information about asset allocation by age, consider reading a detailed blog about this topic on the SoFi website. It will provide you with valuable insights, helping you make informed investment decisions.
4. Assets
Assets are what you invest in—such as stocks, bonds, cash, or real estate. Each asset type carries a different level of risk and return potential. A balanced mix of assets helps reduce overall risk while aiming for steady growth.
5. Dynamic Asset Allocation
Dynamic asset allocation means adjusting your investment mix based on changing market conditions or personal needs. Instead of sticking to a fixed plan, you make periodic changes to take advantage of opportunities or protect against losses. This approach keeps your portfolio flexible and responsive.
6. Financial Goals
Your financial goals define what you want to achieve with your money, such as buying a home, saving for education, or preparing for retirement. Clear goals help shape your investment plan by showing how much you need to save and how long you have to reach it.
7. Liquidity
Liquidity measures how quickly and easily you can turn an investment into cash without losing value. Highly liquid assets, like savings accounts, are great for short-term needs. Less liquid investments, like property, are better suited for long-term growth.
8. Risk
Risk is the possibility that your investment might lose value or not perform as expected. Every investment carries some level of risk, but managing it through diversification and research helps protect your portfolio. The goal is to balance risk and return based on your comfort level.
9. Goal Factors
Goal factors are the specific details behind each of your financial targets—how much money you need, when you need it, and what it’s for. These details guide how aggressively or conservatively you should invest. Aligning your investments with these factors keeps your plan realistic and focused.
How to Allocate Your Assets Strategically

Smart asset allocation helps you balance risk and reward to achieve your financial goals. The right strategy depends on your age, time horizon, and comfort with risk. Here are the most effective ways to allocate your assets wisely:
1. Age-Based Allocation
It is a simpler approach that focuses on adjusting your asset mix as you get older. For example, at the age of 30, you might have 70% of your investment in stocks and the remaining 30% in bonds and cash. But as you get older and reach the age of 60, you might have 40% in stocks and a larger portion of your savings in the form of safer assets.
Example:
- At 30 → 70% stocks, 30% bonds/cash
- At 60 → 40% stocks, 60% bonds/cash
2. Time-Horizon-Based Allocation
Your time horizon determines how long your money can stay invested before you need it.
- Short-term goals (1–3 years): Choose low-risk, liquid assets like savings or money market funds.
- Mid-term goals (3–10 years): Mix bonds with a smaller share of stocks for balanced growth.
- Long-term goals (10+ years): Focus on stocks to build wealth over time.
3. Risk-Based Allocation
Your comfort level with risk should guide your investment choices.
- Conservative investors: Prefer stable returns with more bonds and cash.
- Moderate investors: Combine stocks and bonds for balance.
- Aggressive investors: Focus heavily on stocks for higher potential returns.
4. Dynamic Allocation
Dynamic allocation means adjusting your investments based on changing market conditions or personal goals. It helps you take advantage of new opportunities and protect your portfolio during market downturns. Regularly reviewing your asset mix keeps your investments aligned with your needs.
5. Diversified Allocation
Diversification spreads your investments across different asset types, industries, and regions. This reduces the impact of market volatility and helps maintain steady returns. A well-diversified portfolio protects you from heavy losses if one investment performs poorly.
Important Considerations for Effective Asset Allocation


Even the best investment plan needs regular attention and balance. These key considerations help you stay on track and make the most of your portfolio:
1. Diversification
Diversifying your investments is one of the most effective ways to reduce risk and maintain stability. Never rely on a single type of asset—spread your money across different investments such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and cash. This approach ensures that if one area underperforms, others can balance your returns and keep your portfolio strong.
2. Portfolio Rebalancing
Over time, your asset mix may change due to market movements. Rebalancing means reviewing your portfolio periodically and adjusting it back to your target percentages. This ensures your investments stay aligned with your goals and risk tolerance.
3. Flexibility and Adaptability
Your financial goals and market conditions can change. Be open to adjusting your investment strategy when needed. A flexible approach helps you respond to new opportunities or reduce exposure during uncertain times.
4. Long-Term Perspective
Investing success comes from patience and consistency. Avoid making emotional decisions based on short-term market fluctuations. Focus on your long-term goals, and allow time for your investments to grow.
5. Professional Guidance
If you’re unsure about your investment choices, consider consulting a financial advisor. Expert advice can help you understand risks, explore new opportunities, and build a portfolio that fits your unique needs.
Conclusion
Effective asset allocation is the key to building a strong and balanced investment portfolio. By considering your age, risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals, you can create a strategy that balances growth and security. Regularly diversifying your investments, rebalancing your portfolio, and staying flexible ensures your money works efficiently over time. Whether you’re just starting out or planning for retirement, a thoughtful, strategic approach to asset allocation helps you achieve long-term financial success and peace of mind.